top of page

引言
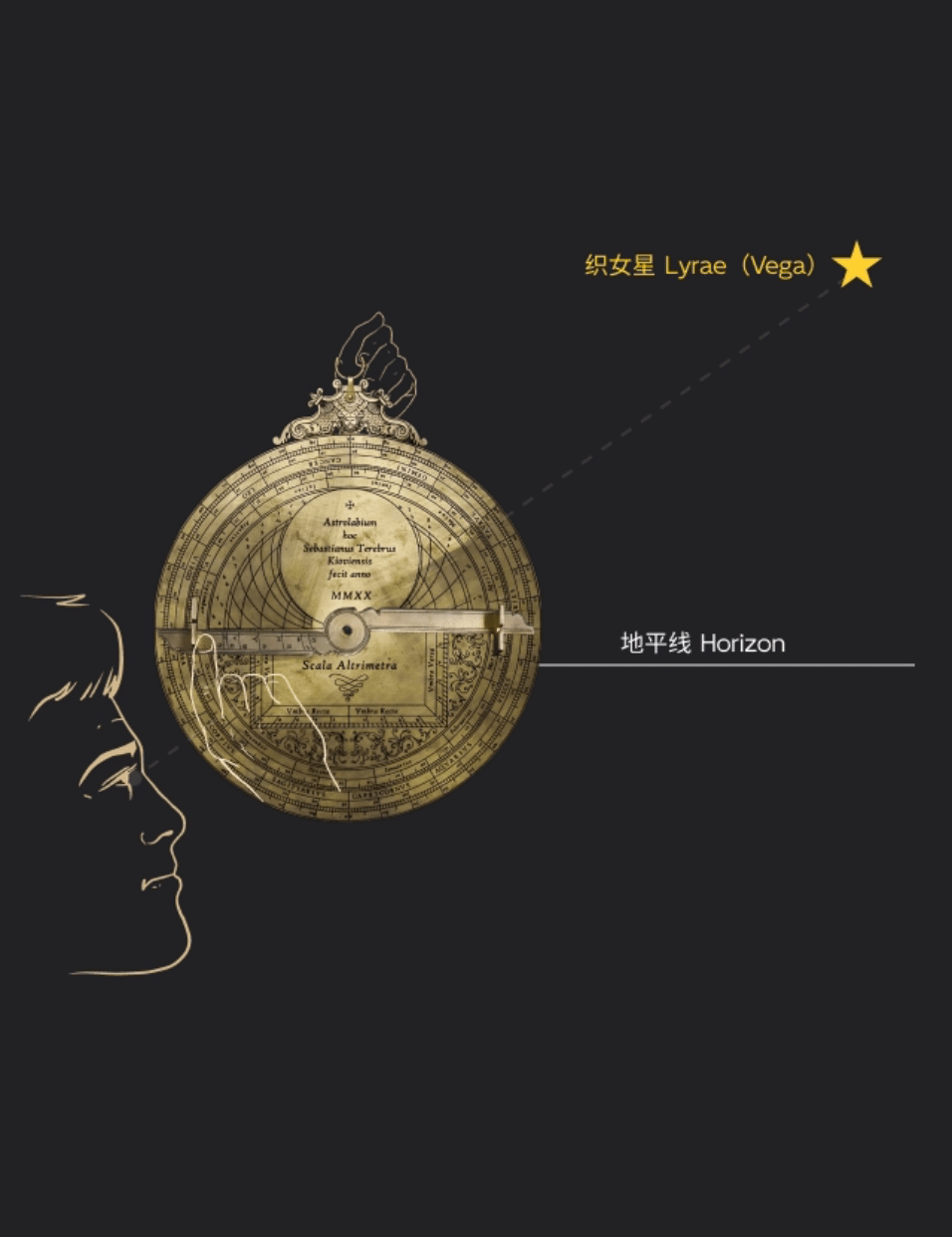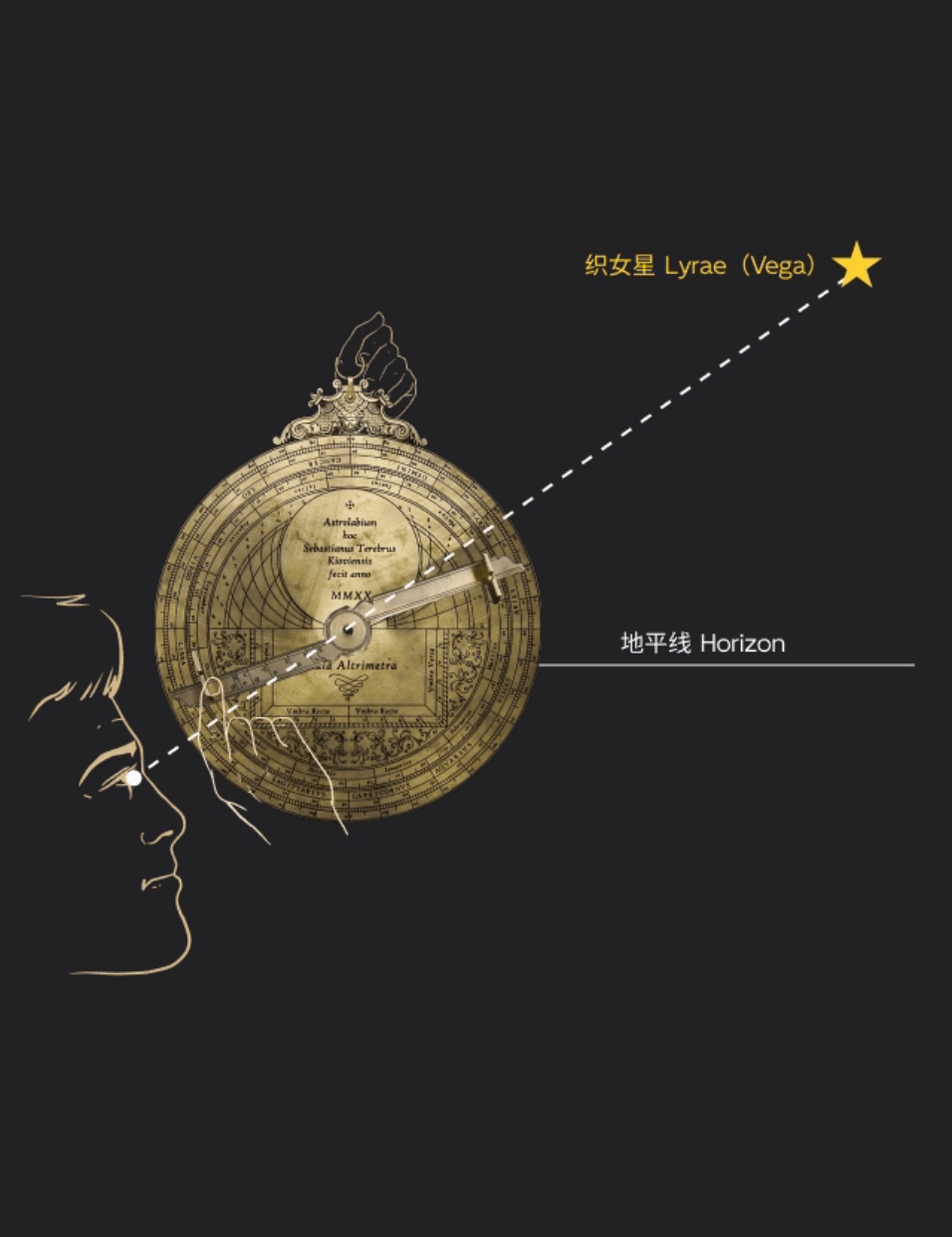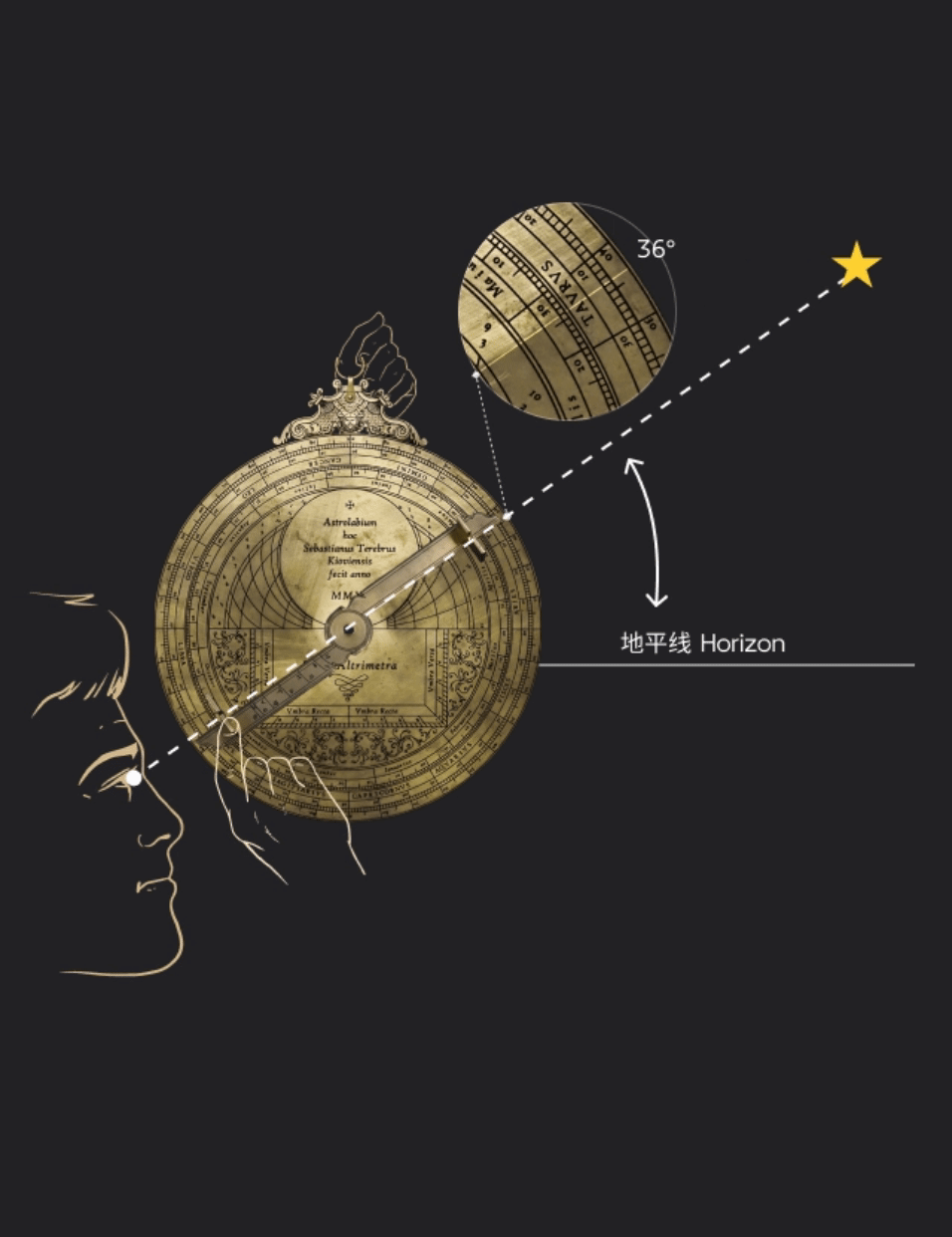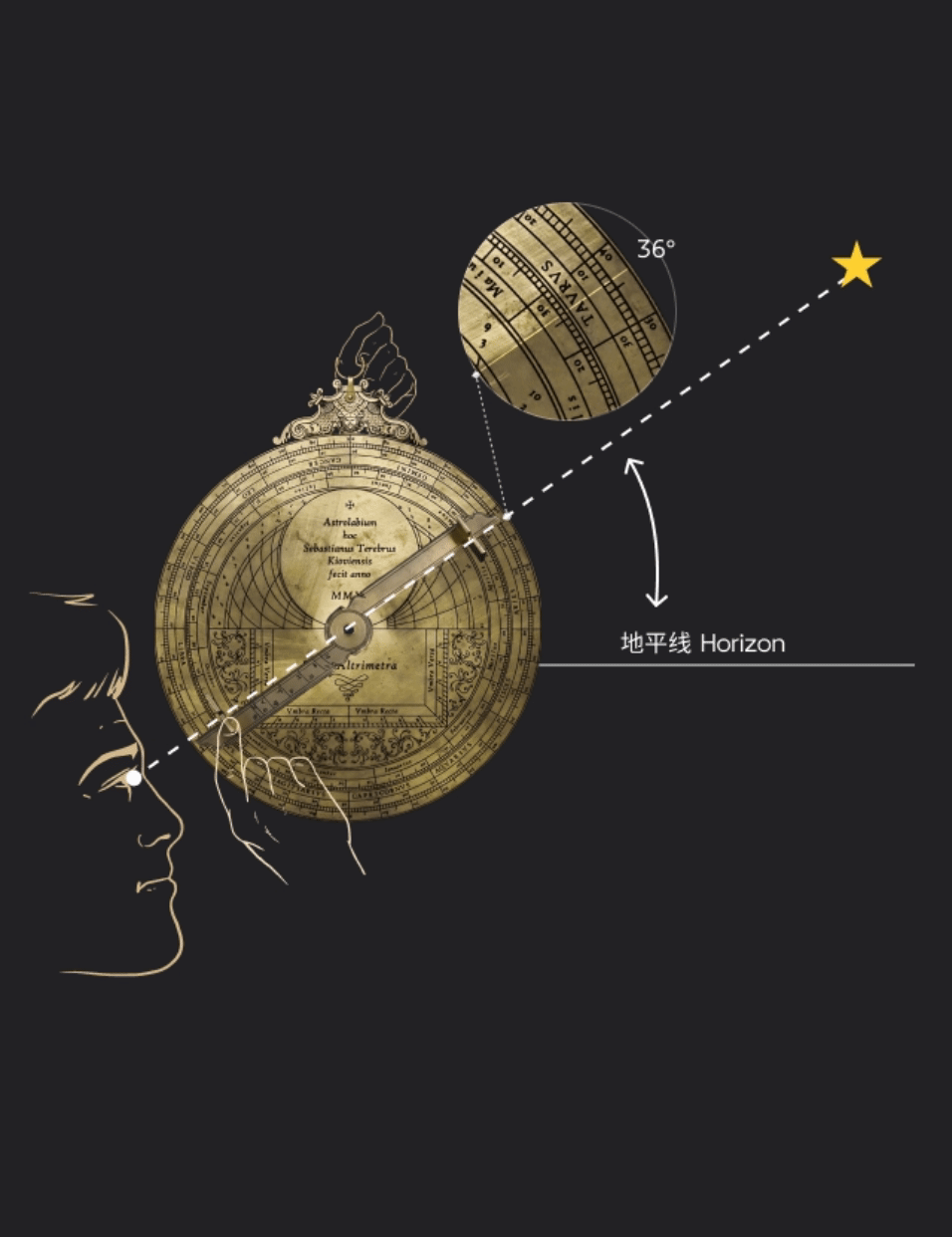
星空浩瀚,令人敬畏。掌握天体运行的规律,是人类孜孜不倦追求的梦想,而星盘正是这种梦想的结晶。西文astrolabe( 即“星盘” )一词,意为“星”(astro)之“持取”(lemma)者。利用球极投影,星盘展示出两球宇宙论的基本图示,是集观测、演示、计时、计算于一体的多功能仪器。
星盘之肇始已不可考,一般认为源于古希腊。它在中世纪伊斯兰世界发扬光大,后传入拉丁西方,得到进一步普及。其间或北至沙俄,或南播非洲,更经由海陆,两度传入中国。星盘不仅是古代天文仪器的代表,更是东西方科技文化交流的明证。
清华大学科学博物馆携手牛津大学科学史博物馆,共同举办此次在线展览,以期揭示星盘的结构、原理、使用方法和历史流变,展现古代天文学的独特魅力。
bottom of page